11-Sep-2025
Gyan Bharatam Mission
News in Shorts
Why in News?
At the first Gyan Bharatam International Conference on 'Reclaiming India’s Knowledge Legacy through Manuscript Heritage’ under the Gyan Bharatam Mission,' the Ministry of Culture invited experts to present research on deciphering the Harappan script.
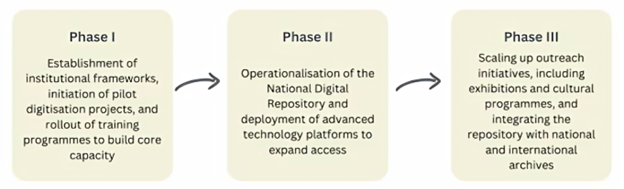
- Announced in Union Budget 2025-26, the Mission aims to preserve, digitise, and disseminate India’s manuscript heritage, blending tradition with technology for future generations.
- Components:
- Nationwide identification and cataloguing of manuscripts.
- Safeguard fragile texts using scientific and traditional methods.
- AI-assisted digitisation and creation of a National Digital Repository.
- Tools like Handwritten Text Recognition and Gyan-Setu AI Challenge.
- Significance:
- Over 44 lakh manuscripts documented in Kriti Sampada, preserving India’s knowledge in various fields.
- Supports Article 51A(f) (fundamental duty) to value & preserve cultural heritage.
- Aligns with NEP, integrating Indian Knowledge Systems into modern education.
Harappan (Indus Valley) Script
|