Why in News?
India and EAEU sign Terms of Reference to begin FTA negotiations, after stalled US trade talks and tariff threats.
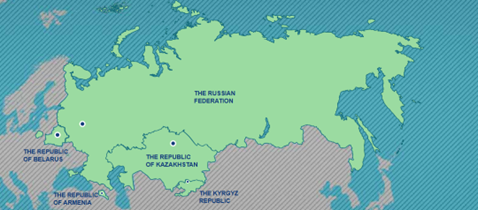
Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)
➔ Establishment: Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (2015)
➔ Members: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia (Largest Member)
➔ HQ: Moscow, Russia
➔ Bilateral Trade (2024): USD 69 bn (up 7% from 2023)
|
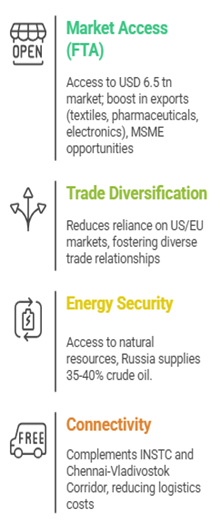
EAEU Significance for India
 |
- High Trade Deficit: With Russia (USD 58.9B in 2024-25), mainly from hydrocarbon imports.
- Geopolitical Sensitivity: Risk of straining NATO/US relations.
- Domestic Industry: Threats from cheap imports; safeguard needed.
- Low FTA Utilization: 25% utilization in India vs 70-80% in developed countries.
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Standards: Strict EAEU regulations hinder Indian agricultural exports.
- Non-Tariff Barriers: Bureaucratic delays, complex customs, regulatory issues.
- Dollar Dependency: Trade still reliant on USD, limited efforts for rupee-ruble usage.
- Strengthening Engagement
- Economic Cooperation: Finalize 2025-2030 program with Russia, extend to all EAEU members (energy, agriculture, industry, education, and culture).
- Diversify Exports: Pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and services - to reduce dependence on hydrocarbons.
- Local Currency Settlement Frameworks: Increase rupee-ruble trade.
- Multilateral Outreach: Engage with BRICS, revive RIC.
- Boost Connectivity: Enhance logistics via INSTC, Northern Sea Route, Chennai–Vladivostok Corridor.
|


