16-Jun-2025
Wind Energy
Environment & Ecology
Why in News?
On Global Wind Day 2025, Union Minister for New and Renewable Energy, Shri Pralhad Joshi, highlighted in a stakeholder conference in Bengaluru that wind energy is central to India’s renewable energy strategy.
(Photo Credit: PIB)
What is Wind Energy?
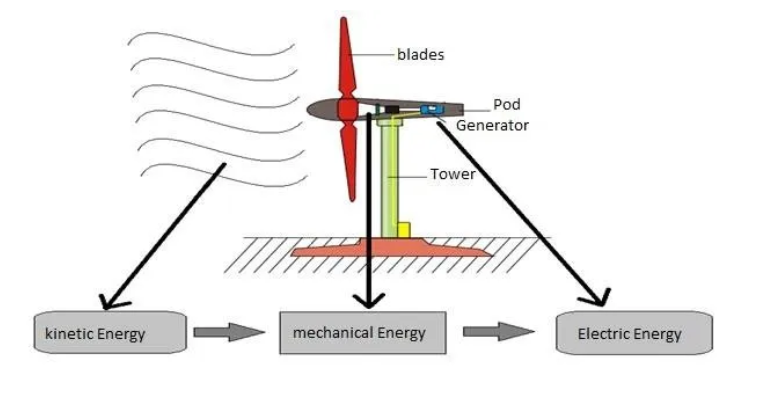
- Wind energy is the kinetic energy of moving air, caused by uneven solar heating, the Earth's surface, and rotation.
- Wind turbines convert this energy into electricity using rotating blades connected to a generator.
Working Principle
- Blades spin when wind blows, creating lift and drag due to air pressure difference.
- This motion turns a generator, producing electricity.
- Gears and shafts increase rotation speed for efficient generation.
Types of Wind Energy Systems
- Onshore: Built on land (e.g., Muppandal Wind Farm in Tamil Nadu).
- Offshore: Installed over water; India is developing one near Gujarat Coast.
- Hybrid: Combines wind with solar for grid stability and better output.
Major Wind Plants in India
|
Wind Farm |
Location |
Capacity (MW) |
|
Muppandal Wind Farm |
Tamil Nadu |
1500 |
|
Jaisalmer Wind Park |
Rajasthan |
1064 |
|
Brahmanvel Wind Farm |
Maharashtra (Dhule) |
528 |
|
Dhalgaon Wind Farm |
Maharashtra (Sangli) |
278 |
|
Vankusawade Wind Park |
Maharashtra (Satara) |
259 |
Government Initiatives: Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018)
National Offshore Wind Energy Policy (2015)
- Aims to use India’s coastline for wind power.
- National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) is the nodal agency for offshore wind development.