04-Jun-2025
Ladakh
Why in News?
President Droupadi Murmu approved 85% reservation in Ladakh by amending the J&K Reservation Act.
About Ladakh
Geographical Features
- Also known as the “Land of Passes”.
- Borders: Tibet (east), Himachal Pradesh (south), Jammu & Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan (west), Xinjiang (north).
- Rivers: Drained by the Indus and its tributaries—Shyok, Nubra, Zanskar, Suru, etc.
- Climate: Cold desert—temperatures range from -40°C to +35°C, low rainfall (10–30 cm), and high solar radiation.
- Soil: Coarse, sandy, alkaline, and low in organic matter.
Strategic Importance
- Became a Union Territory in 2019 after abrogation of Article 370.
- Vital for water security—part of the upper Indus Basin which supports over 200 million people.
- Rich in solar radiation and geothermal potential.
- Growing tourism sector, known as “Lama Land” or “Little Tibet”.
- Connects South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East—key for market access and energy pipelines.
Geopolitical Significance
- Lies on the ancient Silk Route—influencing trade, religion, and culture.
- Resources and strategic location make it a flashpoint among India, Pakistan, and China.
- Important for India's energy, defence, and connectivity needs.
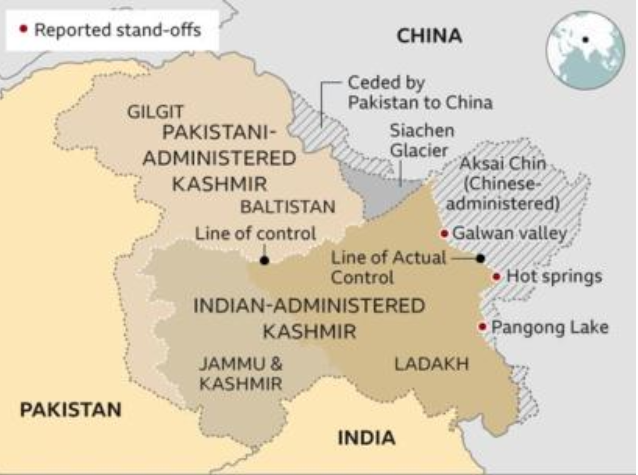
Map: Ladakh
Line of Actual Control (LAC)The Line of Actual Control (LAC) marks the boundary between areas controlled by India and China. While India claims it to be 3,488 km long, China estimates it at around 2,000 km, highlighting the disagreement over its exact length. The LAC in Ladakh emerged due to China’s illegal occupation of Aksai Chin following the 1962 war. This occupation lacks historical or legal justification and remains a point of contention. The LAC is divided into three key sectors:
|
Preparations Through MCQ
Q. Which River primarily drains the Ladakh region along with its tributaries?
(1) Ganga
(2) Brahmaputra
(3) Indus
(4) Yamuna
Answer: (3) Indus