25-Jun-2025
Panchayati Raj Institutions
Indian Polity
Why in News?
Union Home Minister Amit Shah urged CMs of four states to boost gram panchayat revenues, stating it would strengthen the Panchayati Raj system, as per the MHA.
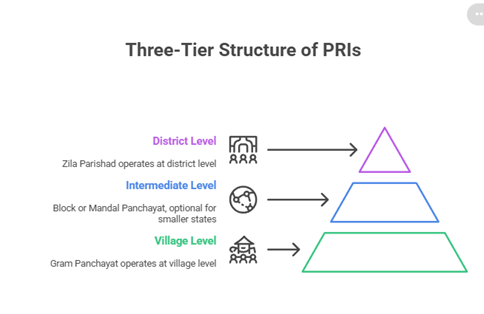
Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)
- PRIs represent rural local self-governance in India, allowing people to directly elect representatives for local governance.
- They form the third tier of government and aim to promote democracy at the grassroots level.
- The system ensures local participation in decision-making, improving accountability and rural development.
Constitutional Provisions
- Article 40 (DPSP): Directed states to set up and empower village panchayats.
- 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992
- Granted constitutional status to PRIs.
- Added Part IX (Articles 243–243O) to the Constitution.
- Introduced the Eleventh Schedule, listing 29 subjects under Panchayat jurisdiction.
Evolution of PRIs
- 1957: Balwantrai Mehta Committee recommended PRIs.
- 1959
- Rajasthan became the first state to implement PRIs.
- Andhra Pradesh followed as the second.
- Early structures varied across states.
- 1992: 73rd Amendment created a uniform structure and made it mandatory for states to implement PRIs.
Constitutionalisation of PRIs
- Based on various committee reports, the 73rd Amendment
- Formalized PRIs under the Constitution.
- Made their structure, powers, and functions legally binding on all states.
Preparing Through MCQWhich Constitutional Amendment Act granted constitutional status to the Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs)? (1) 42nd Amendment Act, 1976 Answer: (3) 73rd Amendment Act, 1992 |