06-Jun-2025
Cold War
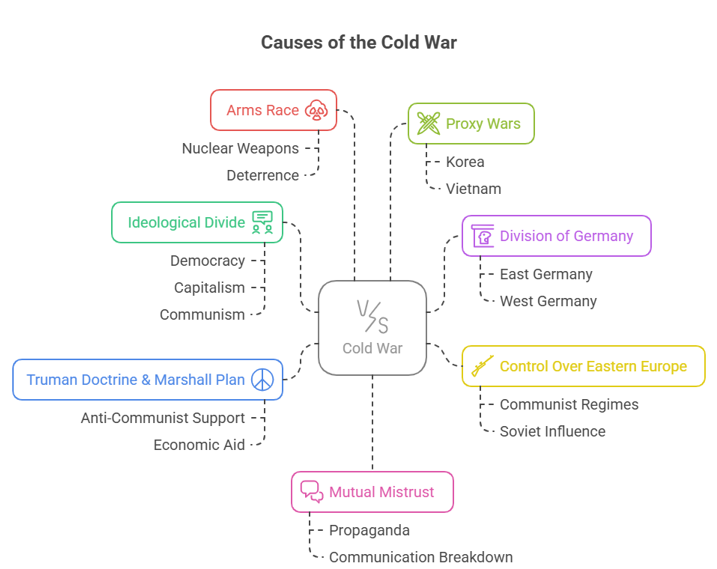
About Cold War
- A global ideological and geopolitical struggle (late 1940s–early 1990s) between the capitalist West (led by USA) and communist East (led by USSR).
- Shaped by doctrines like containment and détente.
- Manifested through:
- Arms race, proxy wars and diplomatic tensions
- Events like Cuban Missile Crisis nearly caused nuclear war
- Led to the collapse of the Soviet Union and changed global alliances.
History of the Cold War
- The Cold War’s roots trace back to the end of World War II.
- At the Yalta Conference (Feb 1945), the USA, UK, and USSR discussed the post-war world.
- They agreed to divide Germany into four zones, each controlled by one Allied power.
- They also decided to form the United Nations to promote global cooperation and avoid future conflicts.
Key Doctrines and Pacts
|
Doctrine/Pact |
Description |
|
Truman Doctrine |
US policy (1947) to contain communism by aiding threatened countries. |
|
Marshall Plan |
US aid (1947) to rebuild Europe and resist communism. |
|
NATO |
Military alliance (1949) of Western democracies for collective defense. |
|
Warsaw Pact |
Soviet-led military alliance (1955) in response to NATO. |
|
Brezhnev Doctrine |
USSR’s right to intervene in socialist countries to maintain communism (1968). |
|
Reagan Doctrine |
US policy (1980s) to support anti-communist groups worldwide. |
|
Iron Curtain Doctrine |
Concept of strict division between East and West during the Cold War. |
End and Consequences of the Cold War
- Ended with Gorbachev’s reforms, Berlin Wall’s fall (1989), and USSR’s collapse (1991).
- US became the sole superpower; Cold War bipolarity ended.
- Eastern Europe turned democratic, and Germany reunified.
- Led to NATO/EU expansion, globalisation, and focus on new global issues.
Important Events of the Cold War
|
Event |
Year(s) |
Description |
|
Berlin Blockade & Airlift |
1948–49 |
USSR blocked West Berlin; US responded with airlift of essential supplies. |
|
Korean War |
1950–53 |
US and USSR supported opposite sides; war ended in a stalemate. |
|
Vietnam War |
1955–75 |
US tried to stop communism; North Vietnam emerged victorious. |
|
Cuban Missile Crisis |
1962 |
USSR placed missiles in Cuba; nuclear war was narrowly avoided. |
|
Space Race |
1957–1969 |
USSR launched Sputnik (1957); US landed on the moon (1969). |
|
Détente |
1970s |
Period of reduced tensions; SALT talks and Helsinki Accords were held. |
|
US-China Rapprochement |
1972 |
US improved ties with China; weakened Soviet influence in Asia. |
India and the Cold War
- Non-Alignment Policy – Stayed out of US/USSR blocs; led NAM movement.
- Active Diplomacy – Mediated tensions, e.g., during Korean War.
- Pro-Soviet Tilt (1960s–70s) – Sought USSR support after 1962 war.
- 1971 Treaty with USSR – Strategic move before Indo-Pak war; not formal alliance.
- Post-Cold War Changes
- 1991 Economic Reforms – Liberalisation, open markets, foreign investment.
- Balanced Foreign Policy – Improved ties with US, maintained Russia ties.
- Multilateralism – Supported inclusive, rule-based global systems.