11-Jun-2025
Evolution of Broadcasting and Satellite Communication in India
Geography
Radio Broadcasting in India
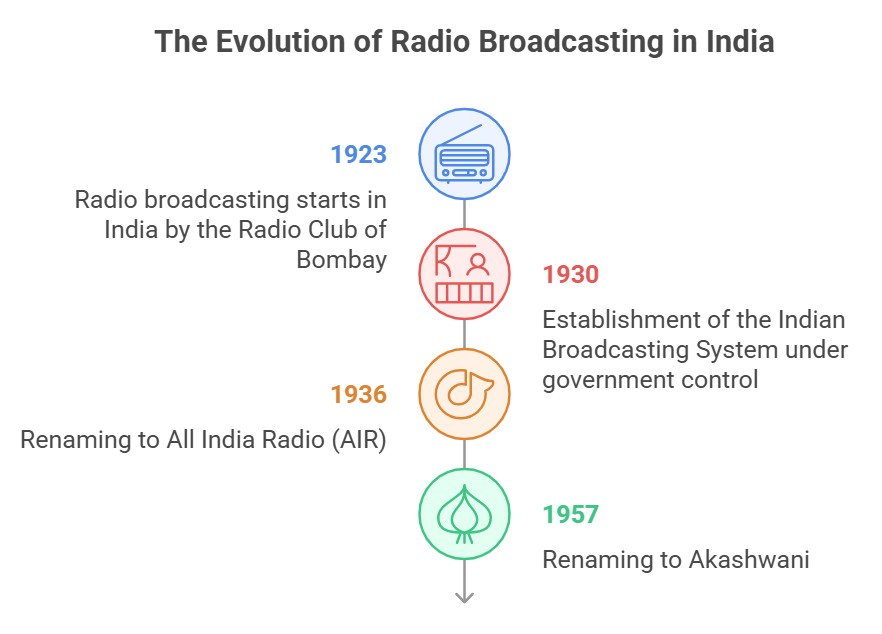
- Beginnings: Radio broadcasting started in India in 1923 by the Radio Club of Bombay.
- Popularity: It gained immense popularity and quickly became a part of every household, transforming the sociocultural landscape of India.
- Government Control: In 1930, the Indian Broadcasting System was established under government control. It was later renamed All India Radio (AIR) in 1936 and Akashwani in 1957.
- Programming: AIR broadcasts a variety of programs, including news, information, educational content, and entertainment. Special news bulletins are aired during events like the Parliament and state legislature sessions.
Television Broadcasting in India
- Introduction: Television broadcasting began in India in 1959, initially limited to the National Capital.
- Expansion: By 1972, several other centres became operational. In 1976, television was separated from All India Radio and received its own identity as Doordarshan (DD).
- INSAT-IA: With the launch of the INSAT-IA satellite in 1983, Doordarshan started Common National Programmes (CNP) and expanded services to remote and rural areas, significantly improving reach and accessibility.
Satellite Communication in India
- Role of Satellites: Satellites serve as both a medium of communication and a regulator of other communication systems, offering a continuous and synoptic view of large areas.
- Importance: Satellite communication has become vital in India due to its role in economic and strategic activities such as weather forecasting, natural calamity monitoring, and border surveillance.
- Satellite Systems
- INSAT (Indian National Satellite System): Established in 1983, INSAT is a multi-purpose satellite system for telecommunications, meteorological observation, and data transmission.
- IRS (Indian Remote Sensing Satellite System): Launched in 1988 with the IRS-IA satellite, it helps in natural resource management and various data collection activities.
- Launch Vehicles: India developed its own Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) for launching satellites.
- Data Collection: Satellites in the IRS system collect data in multiple spectral bands and transmit it to ground stations for processing and utilization, especially by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) in Hyderabad for resource management.