25-Jun-2025
Shaivism and Vaishnavism
History
Why in news
A 15th-century antique lamp, featuring rare Shaiva and Vaishnavaite sculptural carvings, has been discovered at the Anantapadmanabha temple in Perduru, located in the Udupi district of Karnataka.
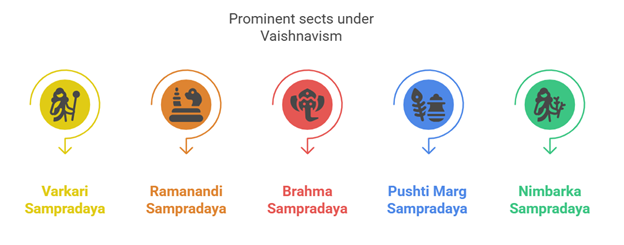
Vaishnavism
- Origin and Growth
- Originated from the Vasudeva-Bhagavata cult during the Gupta period.
- Gradually incorporated other Vedic and Brahmanic deities such as Vishnu and Narayana.
- Historical Background
- Bhagavatism emerged around the same time as Buddhism and Jainism.
- Its roots trace back to Upanishadic philosophy.
- Peak Popularity: Achieved widespread acceptance and became the dominant sect during the Gupta age.
- Philosophy of Avatars: From the later Gupta period, the sect came to be known as Vaishnavism, focusing on the doctrine of incarnations (avatars) of Vishnu.
- Worship of Sakar Form: Emphasized devotion to a personal (Sakar) form of God, mainly Rama and Krishna.
- Role of Alvars
- Alvar saints promoted Ekatmika Bhakti (single-minded devotion) to Vishnu.
- Their devotional songs were compiled as Prabandhas.
Shaivism
- Core Belief
- Shaivism regards Lord Shiva as the Supreme Being.
- Shiva is seen as the creator, preserver, destroyer, revealer, and concealer of everything.
- Early Reference: Panini mentioned a group of Shiva devotees as Shiva-bhagavatas.
- Rise in the South: The Shaiva movement gained momentum in South India through the efforts of 63 saints known as the Nayanars. Nayanars came from various castes, reflecting a socially inclusive movement.
- Literary Contribution: Their devotional Tamil hymns are known as Tevaram Stotras, also referred to as the Dravida Veda.
- Devotional Practices: Devotees apply sacred ash (called bhasma or vibhuti) on the forehead and other body parts as a mark of devotion.
- Philosophical Diversity: Shaivism includes a rich body of texts from various schools of thought,
- Non-dualism (abheda)
- Dualism (bheda)
- Mixed view (bhedābheda) – both dual and non-dual aspects
Preparing Through MCQWhat is the name of the devotional Tamil hymns composed by the Nayanars in the Shaiva tradition? (1) Vedas Answer: (3) Tevaram Stotras |